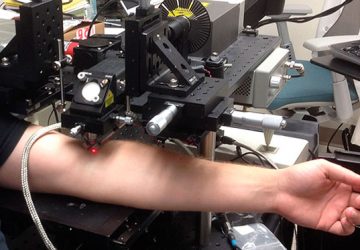
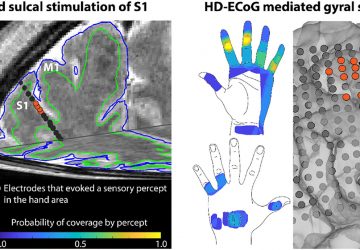
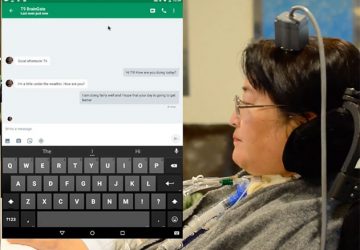
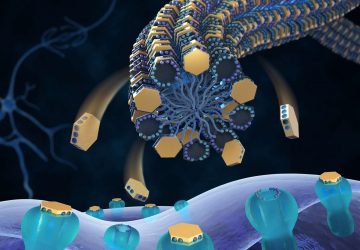
Researchers gain better understanding of how graphene interacts with brain cells to increase neuron activity Image: SISSA While graphene has been tapped to deliver on everything from electronics to optoelectronics, it’s a bit harder to picture how it may offer a key tool for addressing neurological damage and disorders. But that’s exactly what researchers have been looking at lately because of the wonder material’s conductivity and transparency. In the most…
Read MoreDrug-resistant gene goes from pig farms to patients worldwide
A troublesome gene that is resistant to an antibiotic often used as a last resort has been tracked from its origins to hospital patients worldwide in a new study led by UCL and Peking University People’s Hospital. The study, published in Nature Communications, found that the mcr-1 gene, now present across the globe, can be tracked to a single event around 2006 when it moved from pigs into pathogens that…
Read MoreSynthetic Bacteria Drive New Ingestible Gut Sensor
Photo: Lillie Paquette/MIT School of Engineering In the latest edition of “What would you be willing to swallow?”, researchers at MIT today unveiled an ingestible sensor that combines engineered bacteria with ultra-low-power microelectronics to sense changes in the gut. The sensor, roughly the size of a large pen cap, needs to undergo miniaturization and further study before it can be used in humans, but the team hopes to begin a…
Read MoreTiny Robots in Disguise Combat Bacteria in the Blood
Image: Esteban-Fernández de Ávila/ Science Robotics Nanorobots nab bacteria, spherical in shape, that cause a hard-to-treat infection known as MRSA. Researchers have come up with all sorts of ways to propel tiny robots deep into the human body to perform tasks, such as delivering drugs and taking biopsies. Now, there’s a nanorobot that can clean up infections in blood. Directed by ultrasound, the tiny robots, made of gold nanowires with a biological coating, dart around blood, attach to bacteria, and…
Read MoreNew treatment for severe asthma
Researchers from McMaster University and the Firestone Institute for Respiratory Health at St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton, together with colleagues at other partnering institutions, have developed a new method to treat severe asthma. In a study of over 200 participants with severe asthma, the new treatment was shown to have improved asthma symptoms and lung function, while reducing the need for corticosteroids by up to 70%. According to Statistics Canada, 8%…
Read MoreSurgery involving ultrasound energy found to treat high blood pressure
An operation that targets the nerves connected to the kidney has been found to significantly reduce blood pressure in patients with hypertension, according to a clinical trial led in the UK by Queen Mary University of London and Barts Health NHS Trust This is the renal denervation system. Credit: ReCor Medical, Inc. The results are published in The Lancet and have been presented at the EuroPCR congress in Paris….
Read MoreCould Future Nerve Implants Detect and Monitor Illness?
Researchers are intent on decoding body-brain nerve signals to diagnose ailments Credit: Jamie Grill Getty Images Like many of us, Theodoros Zanos hates going to the doctor. A researcher at The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research in Manhasset, N.Y., he tends to avoid his general practitioner unless he’s already sick or in pain. But because he loves his smartphone and other gadgets, he wondered why a piece of hardware couldn’t…
Read MoreDisease tolerance is the key to treating TB, say experts
A new study from McGill University suggests it is the body’s ability to “tolerate” rather than “resist” TB infection that stops symptoms of the disease developing. Credit: Kateryna Kon/Shutterstock.com The study, which was recently published in the journal Science Immunology, lends support to the idea that understanding “disease tolerance” is the key to developing strategies that mitigate the consequences of infection. Historically, scientists’ perspective on host defence against infection…
Read MoreComputers Match Accuracy of Radiologists in Screening for Breast Cancer Risk
Photo: iStockphoto Women with dense breasts have a greater risk of undergoing mammogram screenings that miss signs of breast cancer. That’s why 30 U.S. states legally require that women receive some notification about their breast density. A new study suggests that commercial software for automatically classifying breast density can perform on par with human radiologists: a finding that could encourage wider use of automated breast density assessments. Increased breast density represents “one of the strongest risk…
Read MoreResearchers uncover novel approach for treating neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is the chronic, pathological pain that continues even when the cause of pain is removed. Causes include damage to nerve cells and medicines used to treat cancer. A collaboration between research groups from Indiana University in Bloomington, USA and Turku Centre for Biotechnology in Finland has discovered a novel therapeutic that appears to interrupt the signaling cascades in the body required for multiple forms of neuropathic pain. Neuropathic…
Read More