App by app and tool by tool, scientists are studying whether digital health interventions work, with mixed results As digital health continues to explode on smartphones worldwide, researchers are digging in, trying to figure out which of the new offerings actually work. These scientists aim to determine, using top notch clinical trials, the effectiveness of medical apps, telemedicine and other kinds of digital therapeutics and diagnostics. It’s a big…
Read MoreSynthetic ‘virus’ to kill bacteria
A synthetic ‘virus’ that kills bacteria on first contact has been developed by UCL and National Physical Laboratory researchers (NPL). The study, published in Nature Communications, shows how newly designed proteins can be used to build tiny hollow shells that emulate the outer structures of naturally occurring viruses. The synthetic virus ‘drones’ recognise bacterial cells before targeting and destroying their most vulnerable part – their membrane. “We used high-resolution and…
Read MoreResearchers create first stem cells using CRISPR genome activation
Rendering of DNA. Credit: © polesnoy / Fotolia In a scientific first, researchers at the Gladstone Institutes turned skin cells from mice into stem cells by activating a specific gene in the cells using CRISPR technology. The innovative approach offers a potentially simpler technique to produce the valuable cell type and provides important insights into the cellular reprogramming process. “This is a new way to make induced pluripotent stem cells…
Read MoreUsing light to turn yeast into biochemical factories
In experiments, researchers used light to control yeast. Credit: Sameer Khan/Fotobuddy Scientists have recently learned how to use light to control specific groups of neurons to better understand the operation of the brain, a development that has transformed areas of neuroscience. Researchers at Princeton University have now applied a similar method to controlling the metabolism, or basic chemical process, of a living cell. In a series of experiments, they…
Read MoreNew insight about how viruses use host proteins to their advantage
Viruses have a very limited set of genes and therefore must use the cellular machineries of their hosts for most parts of their growth. A new study, led by scientists at Uppsala University, has discovered a specific host protein that many viruses use for their transport within the cell. The discovery opens up new possibilities to develop a broad spectrum anti-viral therapy. The paper is published this week in PNAS….
Read MoreYeast engineered to manufacture complex medicine
Yeast in petri dish. (stock image) Credit: © sinhyu / Fotolia Stanford University bioengineers have figured out a way to make noscapine, a non-narcotic cough suppressant that occurs naturally in opium poppies, in brewer’s yeast. The researchers inserted 25 foreign genes into the one-celled fungus to turn it into an efficient factory for producing the drug. Many of the inserted genes came from the poppy, but several came from other…
Read MorePaper-folding art inspires better bandages
Ruike Zhao, a postdoc in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, says kirigami-patterned adhesives may enable a whole swath of products, from everyday medical bandages to wearable and soft electronics. Credit: MIT; Image courtesy of researchers; Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license Scraped up knees and elbows are tricky places to securely apply a bandage. More often than not, the adhesive will peel away from the skin with just a…
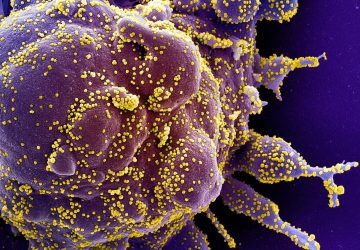
Read MoreThe Fight Against Cancer Is Increasingly Personal
By reclassifying tumors, scientists are finding a path to genuine cancer cures. Here’s an overview of the most promising technologies in immuno-oncology. Colored scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of T lymphocyte cells (smaller round cells) attached to a cancer cell. Credit: Steve Gschmeissner/SPL/Getty Images. Oncology is leading the way in the development of personalized medicines. Over the past two decades, the field has started to move from chemotherapy and radiation…
Read MoreResearchers develop new tool that provides 3D view of metabolic processes
An international team of researchers has developed a computational resource that provides a 3D view of genes, proteins and metabolites involved in human metabolism. Researchers used the tool to map disease-related mutations on proteins and also probed how genes and proteins change in response to certain drugs. The work provides a better understanding of disease-causing mutations and could enable researchers to discover new uses for existing drug treatments. The findings…
Read MoreAI Beats Dermatologists in Diagnosing Nail Fungus
It’s still relatively rare for artificial intelligence to deliver a crushing victory over human physicians in a head-to-head test of medical expertise. But a deep neural network approach managed to beat 42 dermatology experts in diagnosing a common nail fungus that affects about 35 million Americans each year. The latest successful demonstration of AI’s capabilities in the medical field relied heavily upon a team of South Korean researchers putting together a huge dataset of almost…
Read More