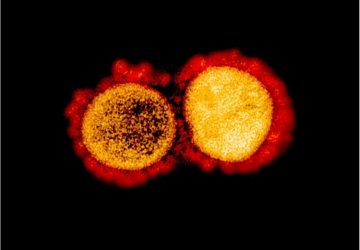
The womb is home to the most complex feat of human biology: the transformation from embryo to fetus to baby. But that magnificent conversion would be impossible without the placenta, the life-giving organ that the developing fetus is tied to via the umbilical cord. Even before a woman knows she’s pregnant, the placenta swells in size, poised to serve as the fetus’s kidneys and liver until the fetus has its…
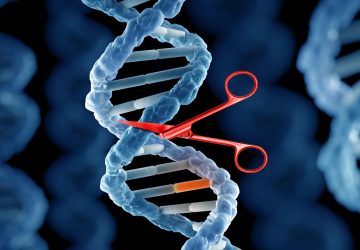
Read MoreGenetic Engineering 2.0: An On-Off Switch for Gene Editing
New, reversible CRISPR method can control gene expression while leaving underlying DNA sequence unchanged. Over the past decade, the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system has revolutionized genetic engineering, allowing scientists to make targeted changes to organisms’ DNA. While the system could potentially be useful in treating a variety of diseases, CRISPR-Cas9 editing involves cutting DNA strands, leading to permanent changes to the cell’s genetic material. Now, in a paper published online…
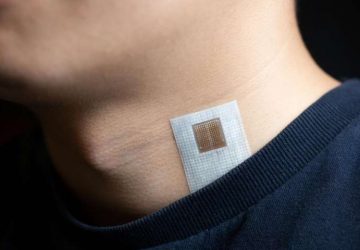
Read MoreCould your smartphone hold clues to early Alzheimer’s disease?
The development of a wearable to detect early Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases years before symptoms show has taken a step closer to reality today, as UK charity Alzheimer’s Research UK announces a partnership with Boston University that will see the first digital data flowing into its global Early Detection of Neurodegenerative diseases (EDoN) initiative. The announcement comes as Alzheimer’s Research UK welcomes over 500 dementia researchers to its annual…
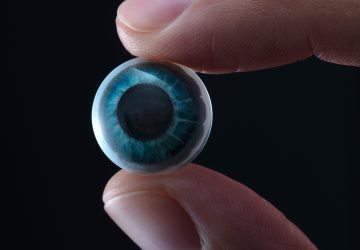
Read MoreMojo Vision Details Low-Power Chips for Augmented Reality Contact Lenses
A millimeter-scale microLED display that fits onto a contact lens to provide augmented reality is, frankly, amazing, but for it to be useful it needs to know what to display. Last month at the IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference, augmented reality contact lens startup Mojo Vision in Saratoga, Calif., reported new details of the image chip and image processing circuits that tell their display what to paint onto your retina….
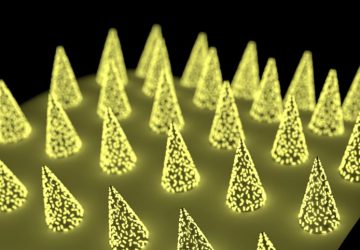
Read MoreNew shape-changing 4D materials hold promise for morphodynamic tissue engineering
New hydrogel-based materials that can change shape in response to psychological stimuli, such as water, could be the next generation of materials used to bioengineer tissues and organs, according to a team of researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago. In a new paper published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, the research team — led by Eben Alsberg, the Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Biomedical Engineering — that…
Read MoreScientists Use Lipid Nanoparticles to Precisely Target Gene Editing to the Liver
Gene editing delivery method in mice suggests possible one shot treatment of high cholesterol The genome editing technology CRISPR has emerged as a powerful new tool that can change the way we treat disease. The challenge when altering the genetics of our cells, however, is how to do it safely, effectively, and specifically targeted to the gene, tissue and organ that needs treatment. Scientists at Tufts University and the Broad…
Read More“Skeleton Key” Can Unlock a Brain: New Realm of Personalized Medicine With Brain Stimulation
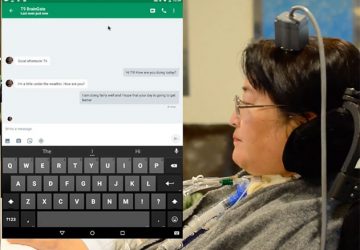
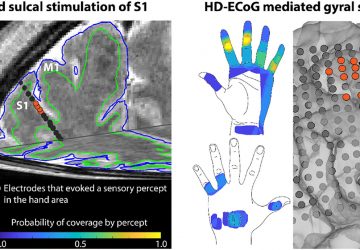
Millions of patients suffering from neurological and mental disorders such as depression, addiction, and chronic pain are treatment-resistant. In fact, about 30% of all major depression patients do not respond at all to any medication or psychotherapy. Simply put, many traditional forms of treatment for these disorders may have reached their limit. Where do we go from here? Research to be published in Nature Biomedical Engineering led by Maryam Shanechi, the Andrew…
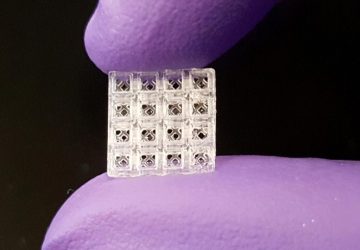
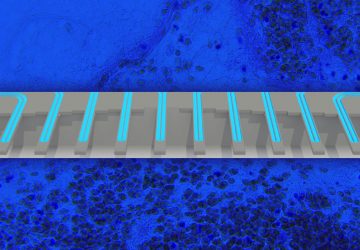
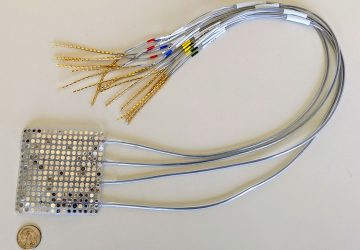
Read MoreNo More Needles for Diagnostic Tests? Engineers Develop Nearly Pain-Free Microneedle Patch
Nearly pain-free microneedle patch can test for antibodies and more in the fluid between cells. Blood draws are no fun. They hurt. Veins can burst, or even roll — like they’re trying to avoid the needle, too. Oftentimes, doctors use blood samples to check for biomarkers of disease: antibodies that signal a viral or bacterial infection, such as SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, or cytokines indicative of inflammation seen…
Read MoreA Shock to the PPE System: New Method for Recharging N95 Masks to Meet COVID Demand
A researcher from the Institute of Industrial Science at The University of Tokyo has demonstrated a novel method for recharging sterilized N95 masks so that they can be reused. By exposing the masks to 100 kilovolts for 3 minutes after sterilization in hot water or an autoclave, they regained their static charge. This work can be rapidly applied to help meet the huge demand for protective equipment that can prevent…
Read MoreStretchable Micro-Supercapacitors That Can Harvest Energy From Human Breathing and Motion
A stretchable system that can harvest energy from human breathing and motion for use in wearable health-monitoring devices may be possible, according to an international team of researchers, led by Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in Penn State’s Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics. The research team, with members from Penn State and Minjiang University and Nanjing University, both in China, recently published its results in Nano…
Read More