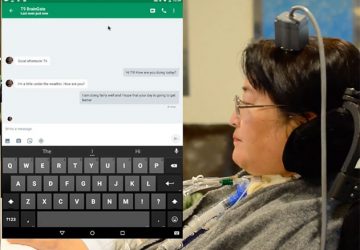
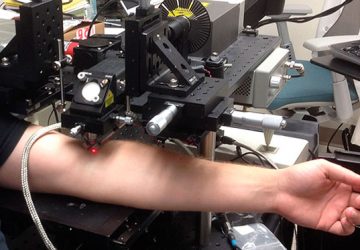
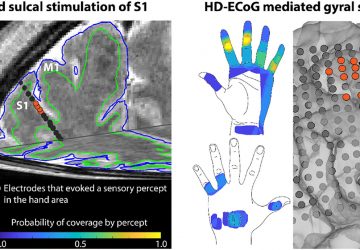
Building on a track record of developing adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors as a groundbreaking clinical tool for gene therapy and gene editing, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) researchers report a more sensitive method for capturing the footprint of AAV vectors — a broad range of sites where the vectors transfer genetic material. By capturing the full range of gene expression patterns caused by AAV vectors, the technique is expected to…
Read MoreRevolutionizing the CRISPR method
Everyone’s talking about CRISPR-Cas. This biotechnological method offers a relatively quick and easy way to manipulate single genes in cells, meaning they can be precisely deleted, replaced or modified. Furthermore, in recent years, researchers have also been using technologies based on CRISPR-Cas to systematically increase or decrease the activity of individual genes. The corresponding methods have become the worldwide standard within a very short time, both in basic biological research…
Read MoreDrone Beats Ambulance in Race to Deliver First Aid to Patients
Medical drones arrived 90 to 120 seconds faster than an ambulance during tests conducted with fake patients placed in Iraq’s busy city streets In Rwanda, drones routinely swoop through the skies, delivering blood products to hospitals. It’s been a medical coup for the drone industry, covered in IEEE Spectrum’s recent feature report. Now, a team in Iraq and Australia has developed another way to use drones in healthcare—as part of a system that detects when an elderly…
Read MoreCheap, Portable Device Uses Quantum Dots to Spot Deadly Bacteria
Recognizing antibiotic-resistant MRSA infections sooner is key to successful treatment Researchers in Australia have developed an inexpensive, portable device that can detect a deadly strain of bacteria in under 40 minutes. The device consists entirely of off-the-shelf and 3D-printed parts that cost a total of US $26, and the results can be read by an app on a smartphone. The developers of the device, at Macquarie University in Sydney, described…
Read MoreResearch team redefines the footprint of viral vector gene therapy
Building on a track record of developing adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors as a groundbreaking clinical tool for gene therapy and gene editing, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) researchers report a more sensitive method for capturing the footprint of AAV vectors — a broad range of sites where the vectors transfer genetic material. By capturing the full range of gene expression patterns caused by AAV vectors, the technique is expected to…
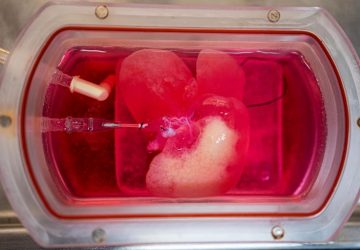
Read More3D printing the human heart
A team of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University has published a paper in Science that details a new technique allowing anyone to 3D bioprint tissue scaffolds out of collagen, the major structural protein in the human body. This first-of-its-kind method brings the field of tissue engineering one step closer to being able to 3D print a full-sized, adult human heart. The technique, known as Freeform Reversible Embedding of Suspended Hydrogels…
Read MoreNew study to ease plight of patients with advanced cancer
Patients with advanced cancer are to test a therapy aimed at reducing their symptoms and improving quality of life. The treatment – called bermekimab – could help with improving outcomes in cancer, including reducing symptoms such as weight loss and decreased mobility. Researchers have been awarded almost £1 million from the Medical Research Council (MRC), part of UK Research and Innovation, to enable the study, which will begin recruiting patients…
Read MoreNew system for precise navigation through the vascular system
Endovascular interventions are an integral part of the medical routine with 6 million procedures done worldwide annually. During the procedure, doctors insert a thin, flexible wire to navigate the catheter into the blood vessels to apply stents or remove blood clots. In order to navigate the catheter precisely through the vessels, patients undergo X-rays during the procedure. One downside is that “patients and doctors are exposed to a considerable amount…
Read MoreResearchers grow active mini-brain-networks
Cerebral organoids are artificially grown, 3D tissue cultures that resemble the human brain. Now, researchers from Japan report functional neural networks derived from these organoids in a study publishing June 27 in the journal Stem Cell Reports. Although the organoids aren’t actually “thinking,” the researchers’ new tool — which detects neural activity using organoids — could provide a method for understanding human brain function. “Because they can mimic cerebral development,…
Read MoreA “biomultimeter” lets scientists measure RNA and protein production in real-time
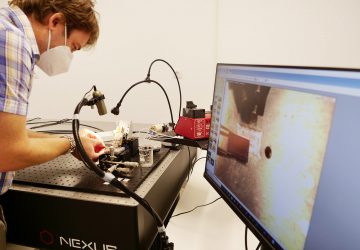
Fluorescent tagging system can expedite the process of designing genes and personalizing medicine. Builders of genetic circuits face the same quandary as builders of digital circuits: testing their designs. Yet unlike bioengineers, engineers have a simple and universal testing tool — the multimeter — that they can touch to their circuit to measure its performance. “There’s nothing remotely like this in bio,” says Peter Carr, a synthetic biologist in MIT…
Read More