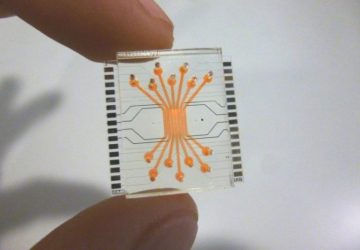
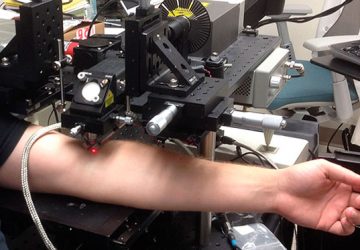
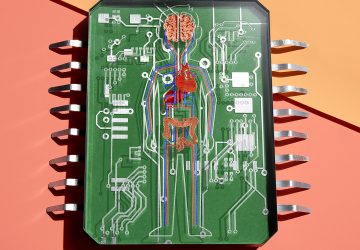
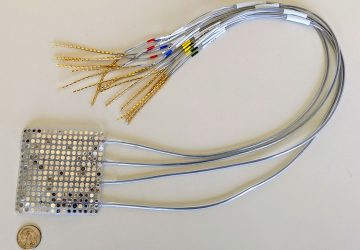
An operation that targets the nerves connected to the kidney has been found to significantly reduce blood pressure in patients with hypertension, according to a clinical trial led in the UK by Queen Mary University of London and Barts Health NHS Trust This is the renal denervation system. Credit: ReCor Medical, Inc. The results are published in The Lancet and have been presented at the EuroPCR congress in Paris….
Read MoreCould Future Nerve Implants Detect and Monitor Illness?
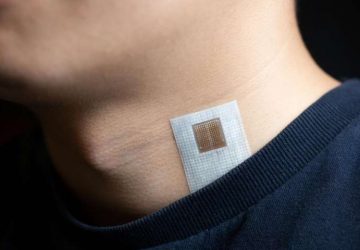
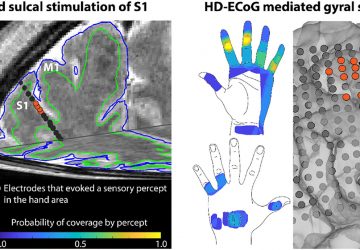
Researchers are intent on decoding body-brain nerve signals to diagnose ailments Credit: Jamie Grill Getty Images Like many of us, Theodoros Zanos hates going to the doctor. A researcher at The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research in Manhasset, N.Y., he tends to avoid his general practitioner unless he’s already sick or in pain. But because he loves his smartphone and other gadgets, he wondered why a piece of hardware couldn’t…
Read MoreDisease tolerance is the key to treating TB, say experts
A new study from McGill University suggests it is the body’s ability to “tolerate” rather than “resist” TB infection that stops symptoms of the disease developing. Credit: Kateryna Kon/Shutterstock.com The study, which was recently published in the journal Science Immunology, lends support to the idea that understanding “disease tolerance” is the key to developing strategies that mitigate the consequences of infection. Historically, scientists’ perspective on host defence against infection…
Read MoreComputers Match Accuracy of Radiologists in Screening for Breast Cancer Risk
Photo: iStockphoto Women with dense breasts have a greater risk of undergoing mammogram screenings that miss signs of breast cancer. That’s why 30 U.S. states legally require that women receive some notification about their breast density. A new study suggests that commercial software for automatically classifying breast density can perform on par with human radiologists: a finding that could encourage wider use of automated breast density assessments. Increased breast density represents “one of the strongest risk…
Read MoreResearchers uncover novel approach for treating neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is the chronic, pathological pain that continues even when the cause of pain is removed. Causes include damage to nerve cells and medicines used to treat cancer. A collaboration between research groups from Indiana University in Bloomington, USA and Turku Centre for Biotechnology in Finland has discovered a novel therapeutic that appears to interrupt the signaling cascades in the body required for multiple forms of neuropathic pain. Neuropathic…
Read MoreNow That Wellness Apps and Telemedicine Are Here, Let’s See If They Work
App by app and tool by tool, scientists are studying whether digital health interventions work, with mixed results As digital health continues to explode on smartphones worldwide, researchers are digging in, trying to figure out which of the new offerings actually work. These scientists aim to determine, using top notch clinical trials, the effectiveness of medical apps, telemedicine and other kinds of digital therapeutics and diagnostics. It’s a big…
Read MoreSynthetic ‘virus’ to kill bacteria
A synthetic ‘virus’ that kills bacteria on first contact has been developed by UCL and National Physical Laboratory researchers (NPL). The study, published in Nature Communications, shows how newly designed proteins can be used to build tiny hollow shells that emulate the outer structures of naturally occurring viruses. The synthetic virus ‘drones’ recognise bacterial cells before targeting and destroying their most vulnerable part – their membrane. “We used high-resolution and…
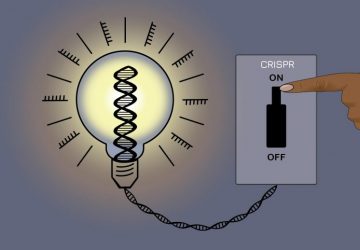
Read MoreResearchers create first stem cells using CRISPR genome activation
Rendering of DNA. Credit: © polesnoy / Fotolia In a scientific first, researchers at the Gladstone Institutes turned skin cells from mice into stem cells by activating a specific gene in the cells using CRISPR technology. The innovative approach offers a potentially simpler technique to produce the valuable cell type and provides important insights into the cellular reprogramming process. “This is a new way to make induced pluripotent stem cells…
Read MoreUsing light to turn yeast into biochemical factories
In experiments, researchers used light to control yeast. Credit: Sameer Khan/Fotobuddy Scientists have recently learned how to use light to control specific groups of neurons to better understand the operation of the brain, a development that has transformed areas of neuroscience. Researchers at Princeton University have now applied a similar method to controlling the metabolism, or basic chemical process, of a living cell. In a series of experiments, they…
Read MoreNew insight about how viruses use host proteins to their advantage
Viruses have a very limited set of genes and therefore must use the cellular machineries of their hosts for most parts of their growth. A new study, led by scientists at Uppsala University, has discovered a specific host protein that many viruses use for their transport within the cell. The discovery opens up new possibilities to develop a broad spectrum anti-viral therapy. The paper is published this week in PNAS….
Read More